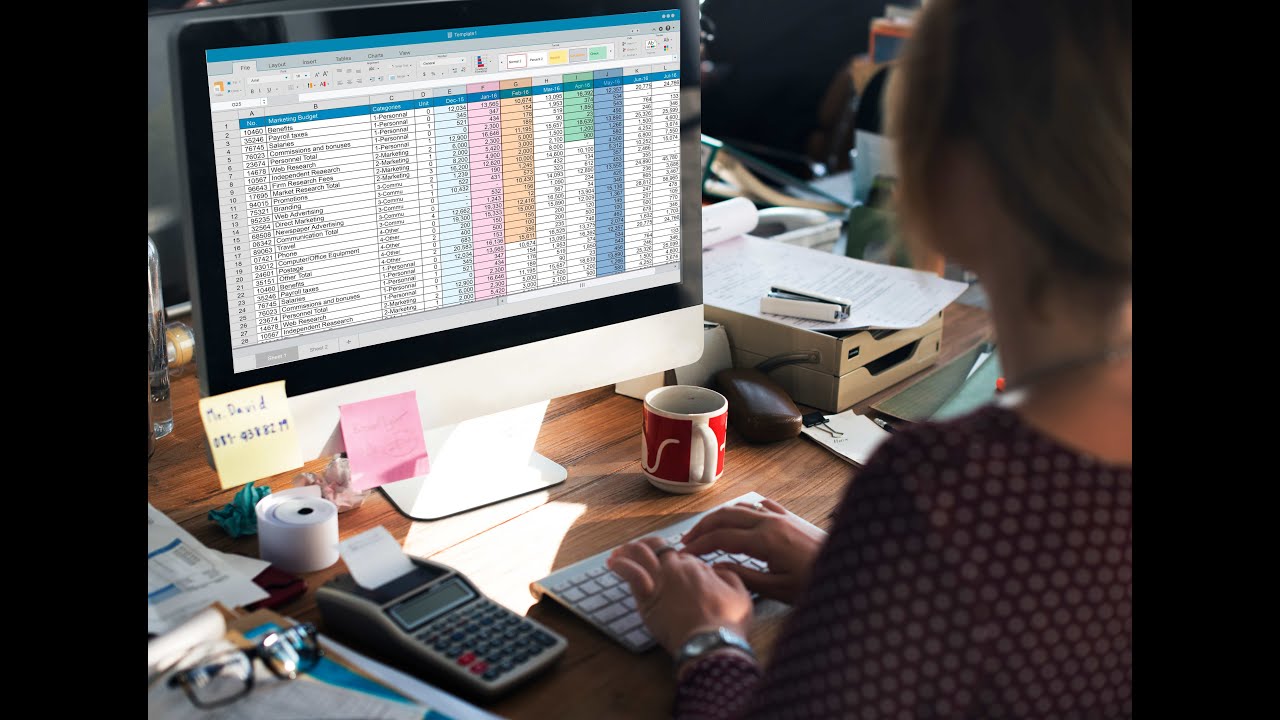
💡 Le saviez-vous ?
Le monde de la technologie évolue rapidement vers le NoCode : maîtrisez simplement votre besoin… et laissez la technologie faire le reste ! 🚀
Aujourd’hui, je vous partage un tutoriel complet et pratique pour :
📱 Créer une application mobile sur mesure
🗄️ Stocker vos données dans une base Microsoft List
📊 Visualiser vos indicateurs et KPI dans un tableau de bord Power BI
Et le plus impressionnant ? 😮
👉 Vous n’avez aucune connaissance en développement à avoir !
Tout se fait facilement grâce aux outils Microsoft :
PowerApps
Microsoft Lists
Power BI
🎯 Un excellent point de départ pour découvrir la digitalisation sans code et automatiser vos processus en toute simplicité.
NoCode #Digitalisation #PowerApps #PowerBI #Microsoft #Automatisation #Innovation #Productivité
The healthcare industry is on the brink of a significant transformation, driven by the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), digital health, and medical technology. The potential of AI in medicine and healthcare innovation is vast, with the capacity to improve patient outcomes, streamline operations, and reduce costs. This article will explore the current state of AI in healthcare, its economic implications, and the potential for future growth. AI has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of healthcare, from diagnostics and treatment to patient monitoring and drug development. For instance, AI-powered diagnostic tools can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, with greater accuracy and speed than human radiologists. AI can also assist in personalized medicine, using genetic data to tailor treatments to individual patients. Furthermore, AI-driven drug discovery platforms can expedite the development of new medications by analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying potential drug candidates. Digital health, or the use of digital technologies to improve healthcare, encompasses a wide range of applications, including telemedicine, mobile health, and health information technology. eHealth, a subset of digital health, focuses on the use of electronic communication and information technologies for health. These technologies enable remote patient monitoring, real-time data collection, and the delivery of healthcare services via the internet. By increasing access to care, improving patient engagement, and reducing costs, digital health and eHealth have the potential to transform the healthcare industry. Health technology, or the application of technology to healthcare, includes a wide range of devices, systems, and methods used to prevent, diagnose, and treat medical conditions. Smart hospitals, a concept that combines health technology with AI, aim to improve patient care, streamline operations, and reduce costs. By using AI-driven systems to manage patient data, automate routine tasks, and optimize resource allocation, smart hospitals can enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. The integration of AI in healthcare has the potential to generate significant economic benefits. According to a report by McKinsey, AI could create $150 billion in annual savings for the US healthcare industry by 2026. These savings could be achieved through increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and improved patient outcomes. Furthermore, AI-driven innovations in drug discovery and development could lead to the creation of new markets and the growth of existing ones. Despite its potential, the implementation of AI in healthcare is not without challenges. These include issues related to data privacy, security, and quality, as well as the need for regulatory oversight and standardization. Additionally, there is a lack of understanding and trust in AI among healthcare professionals and the general public, which must be addressed through education and awareness campaigns. Numerous case studies have demonstrated the potential of AI in healthcare. For instance, Google's DeepMind Health has developed an AI system that can predict acute kidney injury in hospital patients up to 48 hours before it occurs. Similarly, IBM's Watson Health has developed an AI platform that can analyze genomic data to identify potential cancer treatments. These and other examples highlight the potential of AI to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. The future of AI in healthcare is promising, with the potential for continued growth and innovation. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global AI in healthcare market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 44.0% from 2020 to 2027, reaching a value of $61.5 billion. This growth will be driven by increasing demand for personalized medicine, the need for improved healthcare efficiency, and the rise of digital health technologies. The integration of AI in healthcare raises important policy and regulatory considerations. These include the need for clear guidelines on the use of AI in healthcare, the establishment of standards for data privacy and security, and the development of regulatory frameworks for AI-driven medical devices. Additionally, there is a need for policies that support the development and adoption of AI in healthcare, such as funding for research and development, tax incentives, and public-private partnerships. The integration of AI in healthcare has the potential to transform the industry, improving patient outcomes, streamlining operations, and reducing costs. However, this transformation will not be without challenges, and it will require the collaboration of various stakeholders, including healthcare professionals, policymakers, and industry leaders. By working together, we can unlock the full potential of AI in healthcare, ushering in a new era of medical innovation and improving the lives of millions of people around the world.
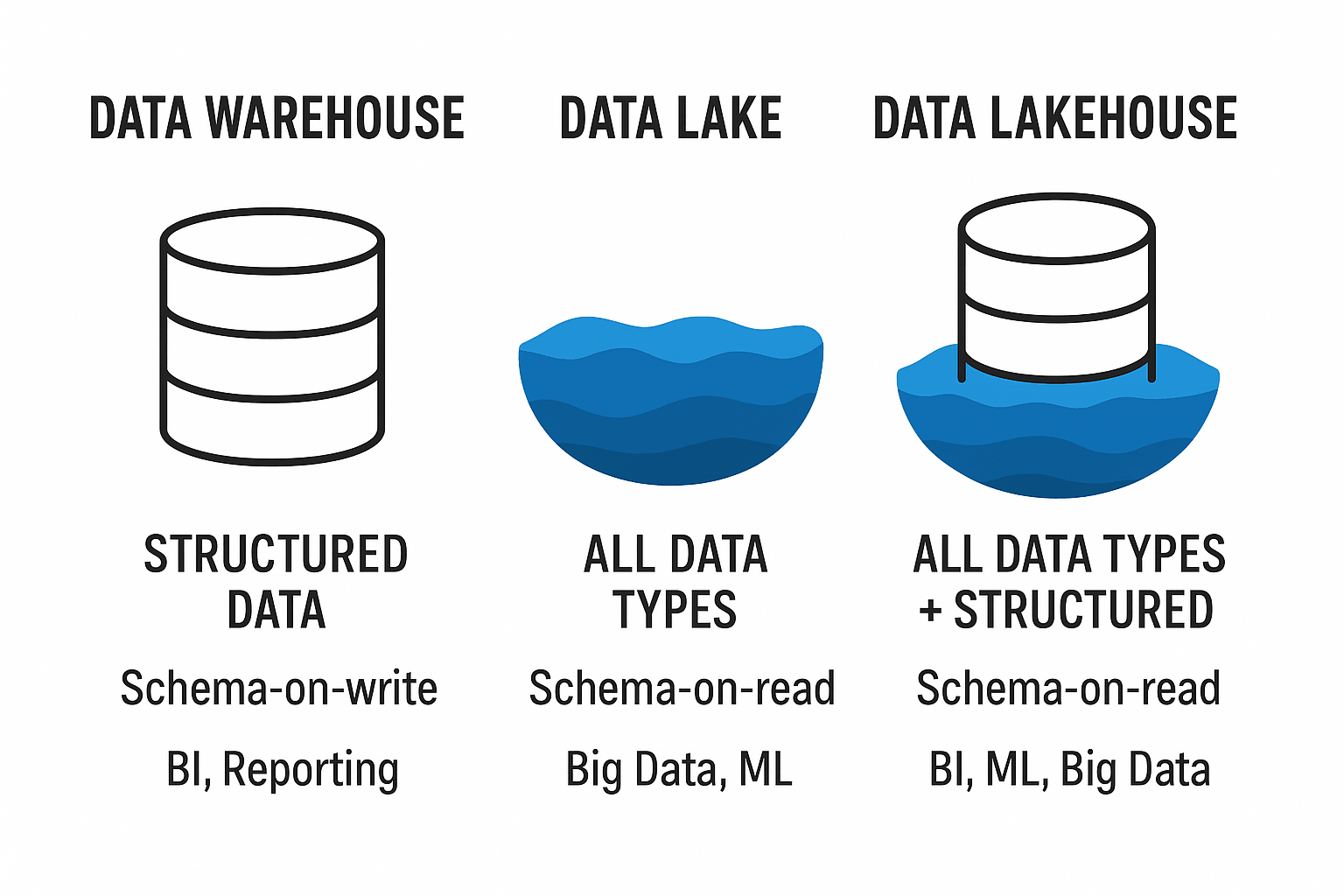
Dans un monde où l’information circule à grande vitesse, la donnée est devenue l’actif stratégique des entreprises et organismes publics. Chaque décision, qu’elle soit opérationnelle ou stratégique, repose désormais sur des informations fiables et disponibles en temps réel. Une mauvaise gestion des données peut entraîner des erreurs coûteuses, ralentir la prise de décision et compromettre la compétitivité. Ainsi, structurer, centraliser et exploiter la donnée est devenu un enjeu majeur.
Les organisations collectent des données provenant de multiples sources : ERP, CRM, systèmes financiers, capteurs IoT, sites web et réseaux sociaux. Ces données peuvent être structurées (tableaux, bases de données), semi-structurées (JSON, XML) ou non structurées (documents, vidéos, emails). La multiplicité de ces sources rend leur consolidation complexe, mais indispensable pour obtenir une vision complète de l’activité.
Les bases de données traditionnelles sont conçues pour stocker des données structurées et gérer des transactions, mais elles montrent leurs limites face à la masse et la diversité des informations modernes. Les traitements sont souvent longs, la scalabilité limitée et le coût élevé lorsqu’il s’agit d’absorber des volumes massifs. Ces contraintes freinent l’analyse rapide et l’exploitation des données pour la prise de décision.
Le Data Warehouse (entrepôt de données) centralise les informations issues de différentes sources, en les structurant pour faciliter l’analyse. Grâce à des processus ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), les données sont nettoyées, organisées et rendues cohérentes. Les entreprises peuvent ainsi produire des rapports fiables, suivre des KPI précis et sécuriser leurs informations. Cependant, les Data Warehouses classiques peinent à gérer les données non structurées et les flux en temps réel.
Le Data Lake permet de stocker toutes les données, brutes ou transformées, structurées ou non, à grande échelle. Cette approche offre une grande flexibilité : les data scientists peuvent explorer librement les données pour des analyses avancées et des projets d’IA. Cependant, l’absence de structure stricte peut rendre la gouvernance et la qualité des données plus difficiles à maintenir.
Le Data Lakehouse combine les avantages du Data Warehouse et du Data Lake : centralisation, gouvernance et qualité des données, tout en conservant la flexibilité et la scalabilité. Il permet le traitement en temps réel, l’analyse avancée et l’exploitation de tous types de données dans un environnement unifié, facilitant le reporting BI et les projets d’intelligence artificielle.
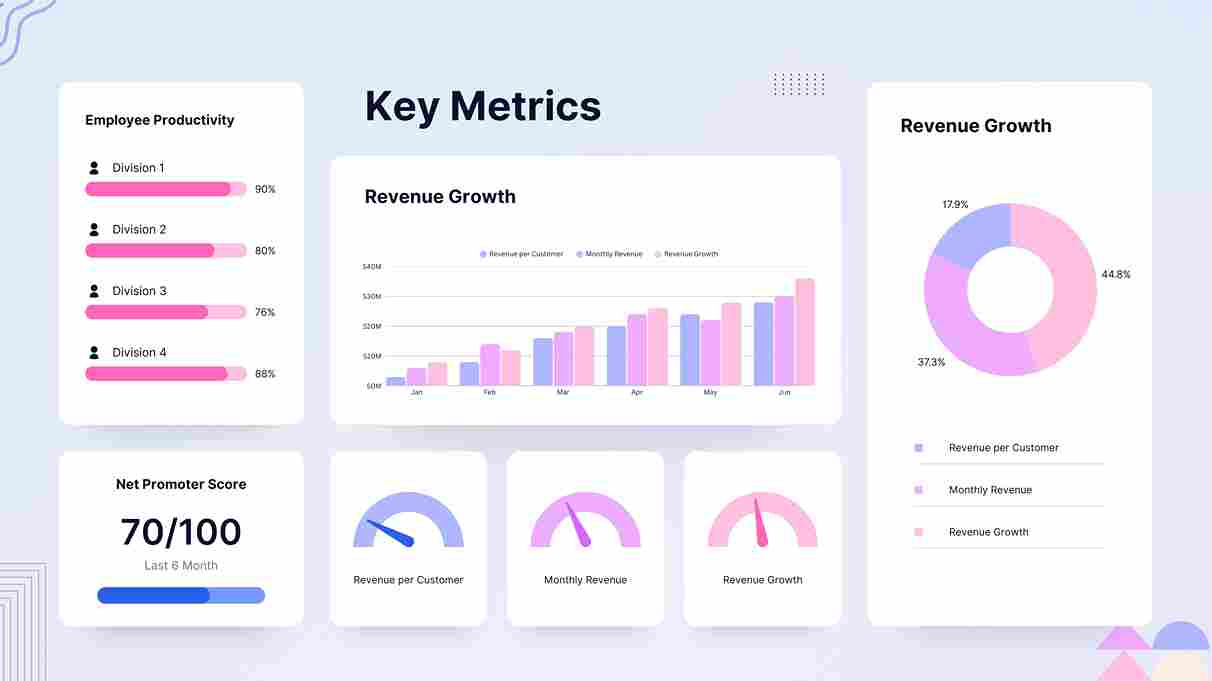
Avec ces architectures modernes, les entreprises bénéficient de données fiables et accessibles rapidement. La BI devient plus efficace : dashboards dynamiques, KPI en temps réel, analyses prédictives et planification stratégique. La qualité et la gouvernance des données sont améliorées, réduisant les risques d’erreurs et garantissant la conformité réglementaire.
Exemples concrets d’usage dans une société multi-sources
- Finance : consolidation des données bancaires et comptables pour un suivi en temps réel.
- Ressources Humaines : analyse des performances, gestion des talents et planification des effectifs.
- Production : optimisation des chaînes de production et maintenance prédictive.
- Marketing : segmentation clients, campagnes personnalisées et analyse des réseaux sociaux.
Ces exemples montrent comment une architecture moderne de gestion de données permet d’exploiter efficacement des sources multiples pour améliorer la performance globale.
Une gestion optimisée des données transforme la prise de décision : elle devient plus rapide, plus précise et mieux informée. Les entreprises peuvent s’appuyer sur l’intelligence artificielle pour anticiper les tendances, optimiser leurs ressources et prévoir la demande. Les décisions stratégiques deviennent alors basées sur des faits et non sur des intuitions, offrant un avantage compétitif considérable.
La donnée est aujourd’hui au cœur de la transformation digitale. Investir dans un Data Warehouse, un Data Lake ou un Data Lakehouse permet de valoriser pleinement cet actif stratégique. Ces solutions offrent rapidité, fiabilité, flexibilité et gouvernance, tout en préparant l’entreprise aux futurs enjeux de l’IA et de l’analytics avancé. Adopter dès maintenant une stratégie data-first est donc essentiel pour rester compétitif et agile dans un environnement multi-sources et en constante évolution.

The rapid growth of wireless technology has brought about a new era of connectivity and convenience, enabling people to access the internet from virtually anywhere. However, this convenience comes with a cost: increased vulnerability to cyber threats. This article will focus on how to secure a Wi-Fi network against cyber threats in a few simple steps, combining both scientific analysis and economic perspectives. To secure a Wi-Fi network, it is essential to understand the basics of Wi-Fi network security. Wi-Fi networks use a variety of security protocols, such as Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), and Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2), to protect the network from unauthorized access. These protocols use various encryption techniques to scramble the data being transmitted over the network, making it difficult for attackers to intercept and understand the data. There are several common cyber threats to Wi-Fi networks, including: * Eavesdropping: Attackers can intercept and read the data being transmitted over the network. * Man-in-the-middle attacks: Attackers can insert themselves between the user and the network, intercepting and altering the data being transmitted. * Denial of Service (DoS) attacks: Attackers can flood the network with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users. * Malware: Attackers can use malware to gain unauthorized access to the network and the devices connected to it. Here are a few simple steps that can be taken to secure a Wi-Fi network: 1. Change the default administrator username and password: Many Wi-Fi routers come with default administrator usernames and passwords that are easily guessable. Changing these to strong, unique passwords can help prevent unauthorized access to the router. 2. Enable WPA2 encryption: WPA2 is the most secure encryption protocol currently available. Enabling WPA2 encryption can help protect the network from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. 3. Use a strong SSID: The SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the name of the Wi-Fi network. Using a strong, unique SSID can help prevent attackers from easily identifying the network. 4. Disable WPS: WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) is a feature that allows devices to connect to the network with the push of a button or by entering a PIN. Disabling WPS can help prevent attackers from easily connecting to the network. 5. Keep the router firmware up to date: Router manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to fix security vulnerabilities. Keeping the router firmware up to date can help protect the network from known vulnerabilities. 6. Use a firewall: A firewall can help protect the network by blocking unauthorized access. 7. Regularly monitor the network: Regularly monitoring the network for unusual activity can help detect and prevent cyber threats. The economic impact of Wi-Fi network security can be significant. A breach of a Wi-Fi network can result in the loss of sensitive data, financial losses, and damage to the reputation of the business or organization. According to a study by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a data breach in the United States is $8.19 million. This includes direct costs, such as legal fees and notification costs, as well as indirect costs, such as lost business and damage to the brand. Governments play an important role in Wi-Fi network security. They can help protect consumers and businesses by establishing regulations and standards for Wi-Fi network security. For example, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States has established regulations for Wi-Fi network security, including requirements for the use of WPA2 encryption and the implementation of firewalls.

In the modern world, smartphones have become an integral part of our daily lives. These devices are not just tools for communication but also platforms for various applications (apps) that cater to our needs and preferences. However, misconfigured and sideloaded apps could turn your phone into a data leak, posing significant security and privacy risks. This article will delve into the scientific and economic implications of this issue. Apps are software programs designed to perform specific tasks on mobile devices. They can be downloaded from official app stores or through sideloading, which involves downloading apps from sources outside the official app store. Misconfigured apps refer to those with incorrect settings, allowing unauthorized access to sensitive data. The risks associated with misconfigured and sideloaded apps include data leakage, unauthorized access to personal information, and increased vulnerability to malware attacks. These risks can lead to financial losses, identity theft, and damage to personal and professional reputation. Misconfigured apps often have incorrect permissions, allowing them to access and transfer data without the user's knowledge or consent. This can occur due to errors in the app's coding or the user's failure to properly configure the app's settings. Research has shown that misconfigured apps are a significant security risk. A study by Gartner found that through 2022, 99% of cloud security failures will be the customer's fault, with misconfiguration being the most common cause. Data leaks can have significant economic consequences. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million. This includes direct costs such as legal fees, IT costs, and customer notification, as well as indirect costs such as damage to brand reputation and loss of customer trust. Moreover, data leaks can lead to financial losses for individuals. For example, in 2017, the Equifax data breach exposed the personal information of 147 million people, leading to a surge in identity theft and financial fraud. Sideloaded apps pose additional security risks. Since they are downloaded from unofficial sources, they may contain malware or other malicious code. A study by Avast found that 99.9% of Android malware is delivered through sideloaded apps. Furthermore, sideloaded apps may not comply with privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). This can lead to legal penalties and damage to the company's reputation. Sideloading involves disabling the security features of the mobile device and downloading apps from sources outside the official app store. This can be done using third-party app stores, direct downloads from websites, or through USB connections. Research has shown that sideloading can significantly increase the risk of malware infections. A study by McAfee found that Android devices with sideloading enabled were 2.5 times more likely to be infected with malware. Malware can have significant economic consequences. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs are expected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2025. This includes direct costs such as IT costs, legal fees, and recovery costs, as well as indirect costs such as damage to brand reputation and loss of customer trust. Moreover, malware can lead to financial losses for individuals. For example, in 2020, the Trickbot malware stole $6 million from bank accounts in the United States. To prevent data leaks and malware infections, users should only download apps from official app stores and ensure that they are properly configured. They should also keep their devices and apps up to date with the latest security patches and use security software. Companies should implement strict security policies and procedures for app development and deployment. They should also conduct regular security audits and provide training for employees on security best practices.

Un projet BI est un projet stratégique pour les entreprises souhaitant améliorer leurs performances et leur compétitivité. Il nécessite une réflexion approfondie, une planification rigoureuse et une mise en œuvre rigoureuse. Les bénéfices sont nombreux et durables, mais les défis sont également importants. Il est donc essentiel de s'appuyer sur des expertises solides et des outils performants pour réussir un projet BI.

In today's digital age, smartphones have become an essential part of our daily lives, storing a vast amount of personal and sensitive data. With the increasing reliance on smartphones, the risk of cyberattacks and data leaks has also grown significantly. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of how to secure a smartphone against cyberattacks and prevent data leaks from an interdisciplinary perspective, combining both scientific research and economic implications. Cyberattacks refer to unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of information or systems. Data leaks, on the other hand, involve the unauthorized release of sensitive or confidential information, often as a result of a cyberattack. In the context of smartphones, cyberattacks can take various forms, such as malware, phishing, spyware, and network spoofing, while data leaks can occur through unsecured Wi-Fi networks, malicious apps, or physical theft. The economic impact of cyberattacks and data leaks can be substantial, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs are expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, with smartphones being a prime target. In addition, a data breach can lead to a loss of customer trust, legal liabilities, and increased insurance premiums. One of the most effective ways to secure a smartphone against cyberattacks and prevent data leaks is by installing security software, such as antivirus, anti-malware, and firewall programs. These programs can detect and remove threats, as well as prevent unauthorized access to the device. Regular software updates are also crucial, as they often include patches for known vulnerabilities and security enhancements. Another layer of protection against cyberattacks and data leaks is the use of strong passwords and biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and iris scanning. Strong passwords should be unique, complex, and changed regularly, while biometric authentication offers a more convenient and secure alternative. Network security is essential in preventing cyberattacks and data leaks, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks. Using a virtual private network (VPN) can encrypt data traffic and mask the user's IP address, providing an additional layer of security. Furthermore, users should avoid sharing sensitive information over unsecured networks and be cautious of suspicious Wi-Fi hotspots. App security is another critical aspect of smartphone security. Users should only download apps from trusted sources, such as the Apple App Store or Google Play Store, and regularly review app permissions. Installing updates for apps and the operating system can also address known vulnerabilities and security issues. Physical security is often overlooked in the context of smartphone security. However, physical theft or loss can lead to data leaks and cyberattacks. Therefore, users should enable features such as remote wipe, lock, and locate, and use physical security measures, such as screen locks and secure storage. Securing a smartphone against cyberattacks and preventing data leaks requires a multi-layered approach, combining both scientific research and economic considerations. By implementing preventive measures, such as security software, strong passwords, network security, app security, and physical security, users can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and data leaks. Ultimately, the cost of implementing these measures is far outweighed by the potential financial and reputational losses resulting from a data breach.