Dans un monde où l’information circule à grande vitesse, la donnée est devenue l’actif stratégique des entreprises et organismes publics. Chaque décision, qu’elle soit opérationnelle ou stratégique, repose désormais sur des informations fiables et disponibles en temps réel. Une mauvaise gestion des données peut entraîner des erreurs coûteuses, ralentir la prise de décision et compromettre la compétitivité. Ainsi, structurer, centraliser et exploiter la donnée est devenu un enjeu majeur.
Les organisations collectent des données provenant de multiples sources : ERP, CRM, systèmes financiers, capteurs IoT, sites web et réseaux sociaux. Ces données peuvent être structurées (tableaux, bases de données), semi-structurées (JSON, XML) ou non structurées (documents, vidéos, emails). La multiplicité de ces sources rend leur consolidation complexe, mais indispensable pour obtenir une vision complète de l’activité.
Les bases de données traditionnelles sont conçues pour stocker des données structurées et gérer des transactions, mais elles montrent leurs limites face à la masse et la diversité des informations modernes. Les traitements sont souvent longs, la scalabilité limitée et le coût élevé lorsqu’il s’agit d’absorber des volumes massifs. Ces contraintes freinent l’analyse rapide et l’exploitation des données pour la prise de décision.
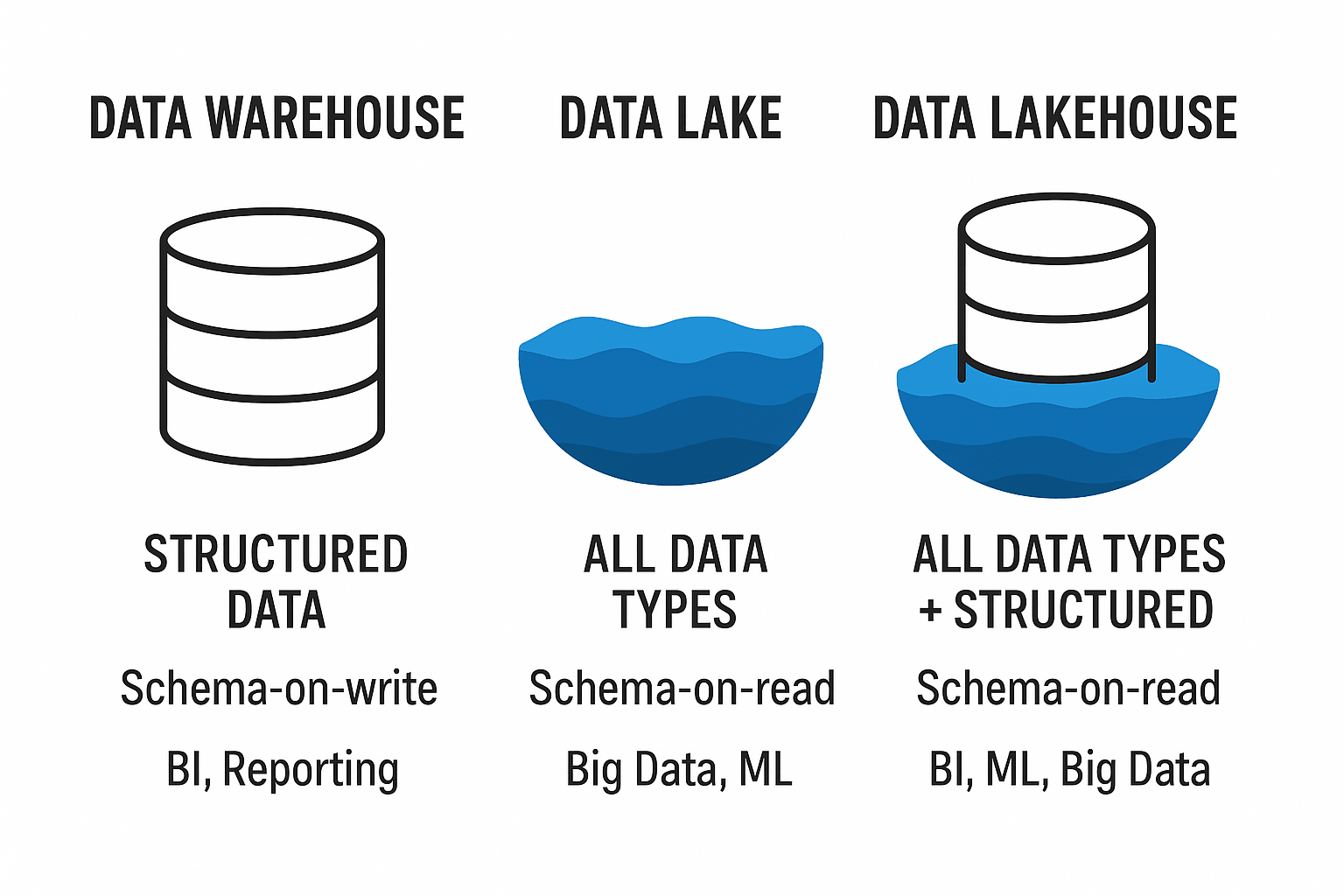
Le Data Warehouse (entrepôt de données) centralise les informations issues de différentes sources, en les structurant pour faciliter l’analyse. Grâce à des processus ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), les données sont nettoyées, organisées et rendues cohérentes. Les entreprises peuvent ainsi produire des rapports fiables, suivre des KPI précis et sécuriser leurs informations. Cependant, les Data Warehouses classiques peinent à gérer les données non structurées et les flux en temps réel.
Le Data Lake permet de stocker toutes les données, brutes ou transformées, structurées ou non, à grande échelle. Cette approche offre une grande flexibilité : les data scientists peuvent explorer librement les données pour des analyses avancées et des projets d’IA. Cependant, l’absence de structure stricte peut rendre la gouvernance et la qualité des données plus difficiles à maintenir.
Le Data Lakehouse combine les avantages du Data Warehouse et du Data Lake : centralisation, gouvernance et qualité des données, tout en conservant la flexibilité et la scalabilité. Il permet le traitement en temps réel, l’analyse avancée et l’exploitation de tous types de données dans un environnement unifié, facilitant le reporting BI et les projets d’intelligence artificielle.
Avec ces architectures modernes, les entreprises bénéficient de données fiables et accessibles rapidement. La BI devient plus efficace : dashboards dynamiques, KPI en temps réel, analyses prédictives et planification stratégique. La qualité et la gouvernance des données sont améliorées, réduisant les risques d’erreurs et garantissant la conformité réglementaire.
Exemples concrets d’usage dans une société multi-sources
- Finance : consolidation des données bancaires et comptables pour un suivi en temps réel.
- Ressources Humaines : analyse des performances, gestion des talents et planification des effectifs.
- Production : optimisation des chaînes de production et maintenance prédictive.
- Marketing : segmentation clients, campagnes personnalisées et analyse des réseaux sociaux.
Ces exemples montrent comment une architecture moderne de gestion de données permet d’exploiter efficacement des sources multiples pour améliorer la performance globale.
Une gestion optimisée des données transforme la prise de décision : elle devient plus rapide, plus précise et mieux informée. Les entreprises peuvent s’appuyer sur l’intelligence artificielle pour anticiper les tendances, optimiser leurs ressources et prévoir la demande. Les décisions stratégiques deviennent alors basées sur des faits et non sur des intuitions, offrant un avantage compétitif considérable.
La donnée est aujourd’hui au cœur de la transformation digitale. Investir dans un Data Warehouse, un Data Lake ou un Data Lakehouse permet de valoriser pleinement cet actif stratégique. Ces solutions offrent rapidité, fiabilité, flexibilité et gouvernance, tout en préparant l’entreprise aux futurs enjeux de l’IA et de l’analytics avancé. Adopter dès maintenant une stratégie data-first est donc essentiel pour rester compétitif et agile dans un environnement multi-sources et en constante évolution.